
CLASS – XII SUBJECT – BIOLOGY
TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS MAXIMUM MARKS:70
General Instructions:
There are a total of 27 questions and five sections in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
Section A contains question numbers 1 to 5, multiple choice questions of one mark each.
Section B contains question numbers 6 to 12, short answer type I questions of two marks each.
Section C contains question numbers 13 to 21, short answer type II questions of three marks each.
Section D contains question numbers 22 to 24, case – based short answer type questions of three marks each.
Section E contains question numbers 25 to 27, long answer type questions of five marks each.
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices are provided in two questions of one mark, one question of two marks, two questions of three marks and all the questions of five marks. A student is to attempt any one of the questions out of the two given in the question paper with the same question number.
SECTION – A
1. Increased IMR and decreased MMR in a population will:
a. Cause rapid increase in growth rate
b. Result in decline in growth rate
c. Not cause significant change in growth rate
d. Result in an explosive population
OR
The male gametes of rice plant have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome number in the female gamete, zygote and the cells of the seedling will be, respectively,
12, 24, 12
24, 12, 12
12, 24, 24
24, 12, 24.
2.In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are:
a. Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 16
b. Phenotypes – 9; genotypes – 4
c. Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 8
d. Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 9
3.According to the Central Pollution Control Board, particles that are responsible for causing great harm to human health are of diameter:
2.50 micrometers
5.00 micrometers
10.00 micrometers
7.5 micrometers
OR
The loudness of a sound that a person can withstand without discomfort is about
a. 150 dB.
b. 215 dB.
c. 30 dB.
d. 80 dB
4.An explant is:
a. Dead plant
b. Part of the plant
c. Part of the plant used in tissue culture
d. Part of the plant that expresses a specific gene.
5.Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important products:
Bacterium Product
(i) Aspergillus niger (a) Lactic acid
(ii) Acetobacter aceti (b) Butyric acid
(iii) Clostridium butylicum (c) Acetic acid
(iv) Lactobacillus (d) Citric acid
Choose the correct match:
i b, ii c, iii d, iv a
i b, ii d, iii c, iv a
i d, ii c, iii b, iv a
i d, ii a, iii c, iv b
SECTION B
6.a. Label the three tiers 1, 2, 3 given in the above age pyramid.
b. What type of population growth is represented by the above age pyramid?
7.A corn farmer has perennial problem of corn-borer infestation in his crop. Being environmentally conscious he does not want to spray insecticides. Suggest a solution based on your knowledge of biotechnology. Write the steps to be carried out to achieve it.
8.How is sex determination in human different from sex determination in bird?
9.Female reproductive organs and associated functions are given below in column A and B. Fill the blank boxes. Define Ovulation.
10.State the principle underlying gel electrophoresis and mention two applications of this technique.
OR
Restriction endonuclease enzymes can cut the DNA at specific sites. These enzymes are produced inside the bacteria. However, the bacteria are not affected by these enzymes. Why? Why are they called restricted enzymes?
11.The pedigree chart given below shows a particular trait which is absent in parents but present in the next generation irrespective of sexes. Draw your conclusion on the basis of the pedigree given below.
12.In a certain population, the frequency of three genotypes is as follows:
Genotypes: BB Bb bb
Frequency: 22% 62% 16%
What is the likely frequency of B and b alleles?
SECTION C
13. What do “Eco”, “R” and “I” refer to in the enzyme EcoRI?
14.Construct a pyramid of biomass of three tropic levels in sea starting with phytoplankton. Is the pyramid upright or inverted? Why?
OR
There is greater biodiversity in tropical /subtropical regions than in temperate region. Explain.
15. Analyse the effects of Alien species invasion on the biodiversity of a given area. Provide two examples.
16. Describe the transcriptional unit with the help of diagram.
17.How does a normal cell differ from a cancer cell? Which process is lacking in cancer cell? Explain the process.
18.A person injured in a road accident and requiring an urgent immune response was brought to a doctor.
19.What did the doctor immediately do?
What kind of immunity was he providing to the patient? Define this kind of immunity.
OR
The following table shows certain diseases, their causative organisms and symptoms. Fill the gaps.
20. State Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. Who proposed it? Is it universally accepted? Explain why?
21. Given below are the events that are observed in an artificial hybridization programme. Arrange them in the correct sequential order in which they are followed in the hybridisation programme.
(a) Re-bagging
(b) Selection of parents
(c) Bagging
(d) Dusting the pollen on stigma
(e) Emasculation
(f) Collection of pollen from male parent.
SECTION D
22. Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, such as RNA and proteins) based on their size and charge. Electrophoresis involves running a current through a gel containing the molecules of interest. Based on their size and charge, the molecules will travel through the gel in different directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from one another.
A. Mention the positive and negative terminals in diagram.
B. What is the charge carried by DNA molecule and how does it help in its separation?
C. How are the separated DNA fragments finally isolated?
23. Many industrial and municipal wastewater treatment plants use bacteria and other microorganisms to help with the process of cleaning sewage. Picking the right bacteria can be tricky since your selection depends on the condition of your area for effective use. Wastewater treatment can also provide a great source for alternative energy if the anaerobic bacteria are handled correctly.
A. Both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are used in sewage treatment plant. Give reason.
B. What will happen if only anaerobic bacteria are used?
C. Used of which type of bacteria will lead to production of activated sludge and energy respectively?
24. Microspores develop in the microsporangium and form mature pollen grains (male gametophytes), which are then used to fertilize female gametophytes. During megasporogenesis, four megaspores are produced with one surviving; the surviving megaspore undergoes mitosis to form an embryo sac (female gametophyte). The sperm, guided by the synergid cells, migrates to the ovary to complete fertilization; the diploid zygote develops into the embryo, while the fertilized ovule forms the other tissues of the seed. Observe the following flow charts and answer the questions:
Pollen mother cell ———>pollen grain———> Vegetative cell + 1 —-2—-> Male gametes
Megaspore mother cell—3—–> Megaspores –4–>Embryo sac—-> Egg
Indicate the stages where mitosis or meiosis occur (2, 3 and 4) in the above flow chart.
Mention the name of cell in 1.
What is the significance of this cell (1)?
SECTION E
25. a.) During reproduction in Human, the chromosome number (2n) is reduced to half (n) in the gametes and again the original number (2n) is restored in the offspring. What are the processes through which these events take place?
b.) Differentiate between spermatogenesis and oogenesis in Human. (3 points)
OR
a.) A human female experiences two major changes, menarche and menopause during her life. Mention the significance of both the events.
b.) Differentiate between spermiation and Spermiogenesis.
c.) Why is breastfeeding recommended during the initial stages of infant growth?
26. a.) In a monohybrid cross of plants with red and white flowered plants, Mendel got only red flowered plants. On self-pollinating these F1 plants got both red and white flowered plants in 3:1 ratio. Explain the basis of using RR and rr symbols to represent the genotype of plants of parental generation. Also show that in this pattern of inheritance both phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio are same.
OR
a.) Can a child have blood group O if his father has blood group ‘A’ and mother blood group ‘B’? Explain.
b.) A hemophilic man marries a carrier woman. Find out the ratio of hemophilic son and daughter.
27. A growth curve given below.
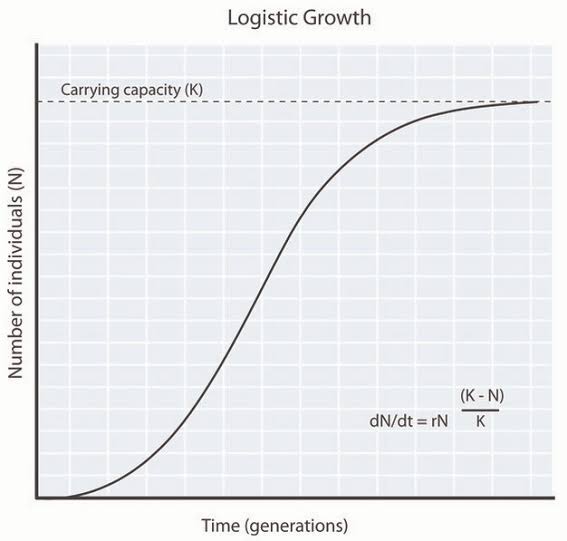
Which type of growth model does it represent?
What is the status of food and space in the above curve? What does K represent?
What does the ‘r’ represent? Give its significance.
OR
What is co-extinction? Explain with a suitable example?
How does in-situ conservation differ from ex-situ conservation?
Mention the two parameters that define Biodiversity hotspot.
